Anatomy definition is not exactly difficult to define. Anatomy, however, is not just about studying and understanding the structure of life on earth. It also has an important role to play in our medical science. Anatomy basically is the branch of physiology concerned with the study of living organisms and their internal parts. It has its origins in prehistoric times, having its roots in the Paleocene period.
The main branches of anatomy are physiology and pathology. Physiology deals with the body's physical functions. It also includes the study of development, reproduction and development of tissues. Pathology mainly deals with disease. The field of pathology is also related to neurology, which is the study of the nervous system.
There are three main types of organs that are associated with physical characteristics. There is a skeletal system, a nervous system and a reproductive system. The skeleton provides structure to all other organs and plays an important role in the functioning of each of them. The nervous system carries out communication between the brain and all other organs. The reproductive system contains organs responsible for the creation of new cells in living things.
Physiological research studies what happens to living organisms and how they function. It describes which organs and tissues are present in the body at different stages of development. He explains the physical, chemical and biological properties of the body that determine its behavior.
The description refers to the classification of the organs of the body according to their function. The classification is based on the location of organs or tissues in the body. The description of the structure and function of organs and tissues is often divided into anatomical, biochemical and functional.
Chemical description is the scientific study of how organisms function by changing their chemical composition. Biochemistry deals with changing the concentration, distribution and activity of chemicals in living organisms. Physiological description of organs and tissues is also divided into two types: structural and functional.
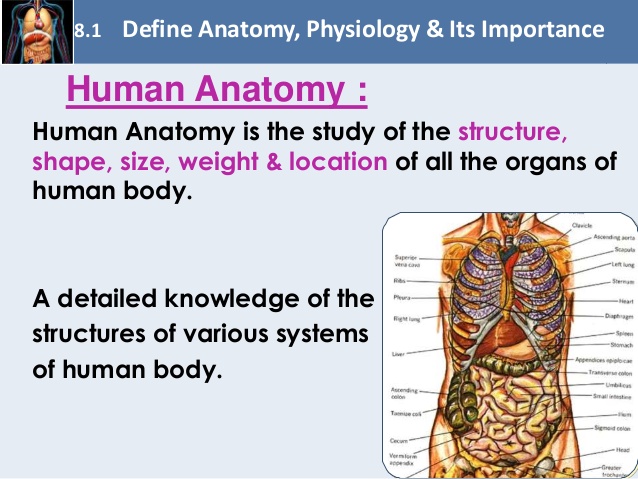
Structural description refers to the description of the structures and functions of the human body. Functional description refers to the description of the functions of the human body. The anatomical description of the human body is also known as the anatomical description.
The human body consists of all the organs, tissues and the various systems and parts. Anatomical structure is described by the three major categories of tissue, organ group. The human body is divided into many layers and each of them have their own purpose. All these are described using the three major categories of tissue, organ group. These categories also have sub-categories.
The most visible part of the human body is the skin, which makes up most of the skeletal structure of the body. The skeletal system consists of the bones and the muscles, while the muscular system comprises the muscles and the connective tissues.
Nerves are the connecting tissues that carry messages from the brain to all the organs, tissues and organs. They also carry messages from the nerves to the tissues and from the tissues to the brain. Every part of the body has a nervous system and it is the responsibility of a nerve to send the signals to all the parts.
The reproductive system also consists of the female and male reproductive organs. When a woman gets pregnant, the baby inside she grows inside her uterus.
The reproductive system also consists of the fallopian tubes, cervical mucus and the fallopian duct. When a woman does not ovulate, a woman cannot get pregnant. The fallopian tubes and the cervix are closed and they store the sperm. This makes the egg to be developed by the female.
The reproductive system is divided into several parts that are responsible for the different stages of pregnancy. The organs and glands responsible for the different stages are identified and the different stages of pregnancy are identified. The process of fertilization takes place in the fallopian tube and the fertilized egg is transferred into the uterus through the cervical mucus.
About the author